More than 20 mutations have been identified in the PLOD1 gene which causes Kyphoscoliosis
Types of EDS. The most common mutation duplicates a large portion of the
gene, resulting in the production of a non-functional version of the ‘lysyl
hydroxylase 1’ enzyme. Several other mutations introduce premature stop signals
that prevent the gene from making any functional enzyme. A loss of lysyl
hydroxylase 1 activity impairs cross-linking between collagen molecules. This
disruption in the network of collagen fibrils weakens connective tissues,
causing the signs and symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Wednesday, June 26, 2013
Tuesday, June 25, 2013
PLOD1 Gene … Normal Function
The PLOD1 gene provides
instructions for making an enzyme called ‘lysyl hydroxylase 1’ — which modifies a particular amino acid called ‘lysine’, one of the
building blocks used to make proteins. Specifically, ‘lysyl hydroxylase 1’ adds
a single oxygen atom to a hydrogen atom to create a charged molecule called a ‘hydroxyl
group’. Hydroxyl groups attach to some of the ‘lysines’ in collagen-like
proteins. We already know that ‘Collagens’ are complex molecules which provide
strength, support and elasticity (the ability to stretch) to many body tissues.
‘Hydroxyl groups’ are essential for collagen
molecules to form stable interactions — called cross-links — with one another. Cross-links between these molecules allow collagen to
form networks of strong, slender fibrils, which are an important part of the
normal structure of connective tissue which binds and supports the body's muscles,
ligaments, organs, and skin.
Monday, June 24, 2013
PLOD1 Gene … Location
Cytogenetic
Location : 1p36.22
Molecular
Location : Chromosome 1
Base pairs (Bp) 11,994,723 - 12,035,598
The PLOD1 gene is located on the
long (q) arm of ‘chromosome 1’ at
position 36.22, more precisely, from BP 11,994,723 ~ 12,035,598 on
chromosome 1.
Sunday, June 23, 2013
PLOD1 Gene ... Official name
PLOD1 gene is responsible for 'Kyphoscoliosis Types'.
Official Name : procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1
Official Symbol : PLOD1
Other names of COL5A2 Gene
@
Collagen Lysyl
Hydroxylase
@
LH
@
LH1
@
LLH
@
Lysine
2-Oxoglutarate Dioxygenase
@
Lysine
Hydroxylase
@
Lysyl
Hydroxylase
@
PLOD
@
PLOD1_HUMAN
@
Procollagen-L-lysine,2-oxoglutarate:oxygen
oxidoreductase (5-hydroxylating)
@
procollagen-lysine
1, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1
@
procollagen-lysine,
2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase (lysine hydroxylase, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type
VI)
@
Protocollagen
Lysyl Hydroxylase
Monday, June 17, 2013
How COL3A1 Gene Cause EDS?
More than 320 mutations in the COL3A1 gene cause the
‘Vascular Type’ of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS). Only a few of these mutations
have been seen in more than one family. The mutations alter the structure and
production of type III procollagen molecules. As a result, a large percentage
of type III collagen molecules are assembled incorrectly or the amount of type
III collagen is greatly reduced.
As per research, these changes affect tissues which
are normally rich in this type of collagen such as the skin, blood vessels, and
internal organs. Lack of sufficient type III collagen causes the signs and
symptoms of ‘Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome’.
Sunday, June 16, 2013
COL3A1 Gene … Normal Function
Type III collagen is found in tissues such as the skin, lungs, intestinal walls, and the
walls of blood vessels. The COL3A1 gene produces the components of
type III collagen, called pro-alpha1 (III) chains. 3 copies of this chain
combine to make a molecule of type III procollagen. These triple-stranded,
rope-like procollagen molecules must be processed by enzymes outside the cell
to remove extra protein segments from their ends. Once these molecules are
processed, the collagen molecules arrange themselves into long, thin fibrils.
Within these fibrils, the individual collagen molecules are cross-linked to one
another. These cross-links result in the formation of very strong mature type
III collagen fibrils, which are found in the spaces around cells.
Saturday, June 15, 2013
COL3A1 Gene … Location
Cytogenetic
Location : 2q31
Molecular
Location : Chromosome 2
Base pairs (Bp) 189,839,098 - 189,877,471
The COL3A1 gene is located on
the long (q) arm of ‘chromosome 2’ at
position 31, more precisely, from BP 189,839,098 ~ 189,877,471 on
chromosome 2.
Friday, June 14, 2013
COL3A1 Gene ... Official Name
COL3A1 gene is responsible for 'Vascular Types', most
severe form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS)
Official Name : Collagen,
type III, alpha 1
Official Symbol : COL3A1
Other names of COL5A2 Gene
@
alpha 1 type
III collagen
@
CO3A1_HUMAN
@
collagen,
fetal
@
Collagen III,
alpha-1 polypeptide
@
Collagen, type
III, alpha 1 (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV, autosomal dominant)
@
EDS4A
Thursday, June 13, 2013
How COL5A2 Gene Cause EDS?
Mutations
in the COL5A2 gene have been identified in a small number of
patients with classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). These mutations change the
structure and function of the pro-alpha2 (V) chain. As a result, type V
collagen fibrils in the skin which are assembled with the altered protein are
large and irregular.
Research
is going on how these changes in collagen structure cause the signs and
symptoms of classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS).
Wednesday, June 12, 2013
COL5A2 Gene … Normal Function
We
already discussed about the ‘Collagen Protein’ in our COL5A1 gene discussion.
The COL5A2 gene
produces a component of type V collagen, called the pro-alpha2 (V) chain. 1
pro-alpha2 (V) chain combines with 2 pro-alpha1 (V) chains (produced by the COL5A1 gene)
to form ‘Type V pro-collagen’.
These
triple-stranded, rope-like pro-collagen molecules must be processed by enzymes
outside the cell. Once these molecules are processed, they arrange themselves
into long, thin fibrils that cross-link to one another in the spaces around
cells. The cross-links result in the formation of very strong, mature type V
collagen fibers.
As
we discussed earlier ‘Type V collagen’ also plays a role in assembling other
types of collagen into fibrils within many connective tissues.
Tuesday, June 11, 2013
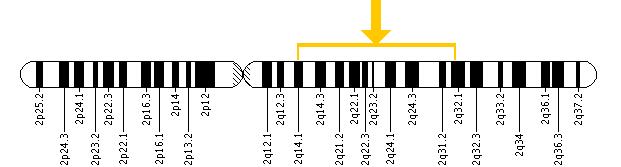
COL5A2 Gene … Location
Cytogenetic Location : 2q14-q32
Molecular Location : Chromosome 2
Base pairs (Bp) 189,896,640 - 190,044,604
The COL5A2 gene is located on
the long (q) arm of ‘chromosome 2’ between
positions 14 and 32, more precisely, from BP 189,896,640 ~ Bp 190,044,604
on chromosome 2.
Monday, June 10, 2013
COL5A2 Gene ... Official Name
The 2nd gene responsible for 'Classic
Types' of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is COL5A2.
Official Name : Collagen, type
V, alpha 2
Official
Symbol : COL5A2
Other names of COL5A2 Gene
@
AB collagen
@
CO5A2_HUMAN
@
Collagen,
fetal membrane, A polypeptide
@
Collagen V,
alpha-2 polypeptide
Thursday, June 6, 2013
How COL5A1 Gene cause EDS …
More than 50% of cases of classical Ehlers-Danlos
syndrome (EDS) are caused by mutations in the COL5A1 gene. Many of
these mutations lead to a non-functional/absent pro-alpha1 (V) chain. As a
result, type V collagen fibrils in the skin and other tissues cannot be
assembled correctly. The fibrils are disorganized and larger than usual.
Research is going on how these changes in collagen
structure cause the signs and symptoms of classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
(EDS).
Wednesday, June 5, 2013
COL5A1 gene ... Normal Function
Collagens form a family of proteins which
strengthen & support many tissues in the body such as skin, ligaments,
bones, tendons, muscles and the extracellular matrix between cells &
tissues.
The COL5A1 gene
produces a component of type V collagen — pro-alpha1 (V)
chain. 3 of these chains combine to make a molecule of type V pro-collagen.
Alternatively, 2 of these chains can also combine with 1 pro-alpha2 (V) chain
(produced by the COL5A2 gene) to form type V pro-collagen.
These triple-stranded rope-like pro-collagen
molecules must be processed by enzymes outside the cell. Once these molecules
are processed, they arrange themselves into long, thin fibrils that cross-link
to one another in the spaces around cells. The cross-links result in the
formation of very strong, mature type V collagen fibers.
Type V collagen also plays a role in assembling
other types of collagen into fibrils within many connective tissues and also
essential for the formation of normal type I collagen fibrils.
Sunday, June 2, 2013
COL5A1 Gene ... Location
Cytogenetic Location : 9q34.2-q34.3
Molecular Location : Chromosome 9 :
Base pairs (Bp) 137,533,651 -
137,736,688
The COL5A1 gene is located on the long (q) arm of ‘chromosome 9’ between positions 34.2 and 34.3, more precisely, from BP 137,533,651 ~ Bp 137,736,688 on chromosome 9.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)